Confused on what to buy between a Laptop and Desktop? Make an energy-efficient choice by reading the difference in the energy consumption of Laptop vs Desktop.

Published on 24/09/2023
By Parneet Kaur
Energy Comparison
Over the years, the thrive in technology has been swift and how! With that, the world has turned to Laptops or Desktops for work purposes, education, or simply to indulge in a fun gaming sesh. However, one decade-long debate that still makes you scratch your head when you set out to buy them is: which one is better suited for you? Or for that matter, how do you even tell the two apart?
There are many factors to be considered when you're looking to navigate the difference such as price, portability, space, and upgrade. But one factor that we often fail to reflect on is the energy consumption of Laptop vs Desktop. The skyrocketing power bills, after all, have lately been no ordinary concern for Aussies.
While we can’t rescue your pockets entirely from them, we sure can help you save some hard-earned bucks by walking you through the ultimate showdown of Laptop vs Desktop: energy consumption.
We have laid out a few parameters that compare the energy consumption of laptop vs desktop side by side. Take a quick look at our comparative analysis and judge the more energy-efficient device yourself:
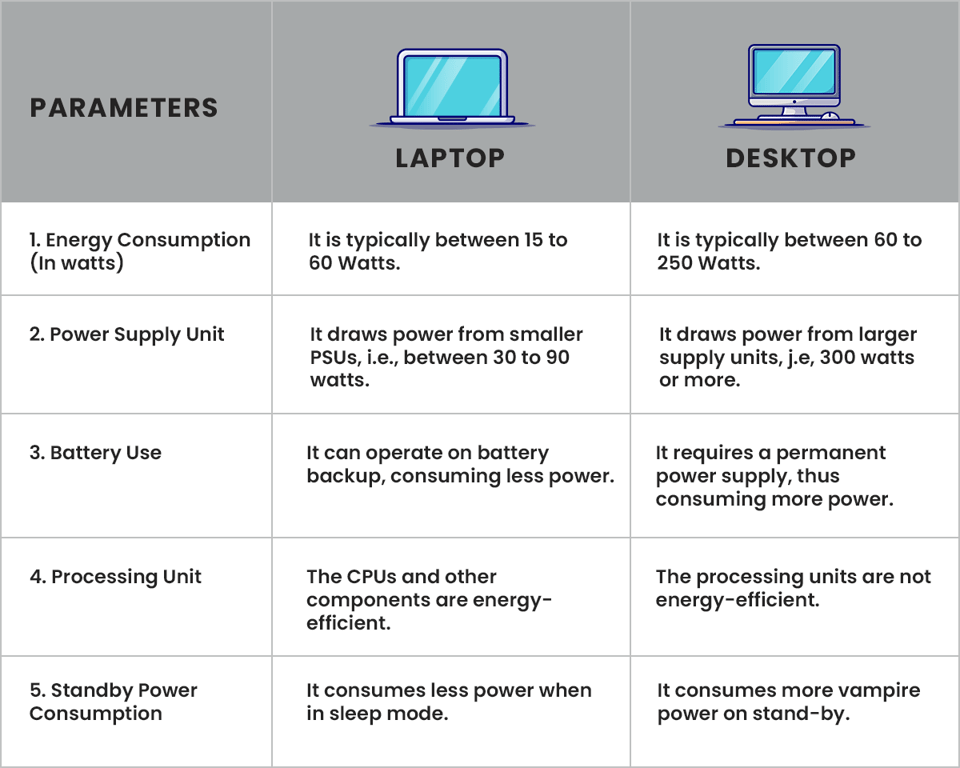
First and foremost, the energy consumption of laptop vs desktop largely differs from one another. It is typically measured in watts, i.e., the standard unit of power.
A Laptop takes the bigger piece of the cake in this battle since it is known to consume 80% less electricity than desktop. Figuratively speaking, it takes up anywhere between 15 to 60 Watts. So, if say, the laptop is running straight for eight hours in a day, its consumption would vary between 150 to 300 kWh/year. However, remember that you have the option to decrease this laptop power usage by switching to power saver modes.
A Desktop, on the other hand, consumes an average of 60 to 250 Watts of electricity. In case you’re confused, let us break it to you that this PC power consumption is the complete sum of the average consumption of the computer, the internet modem, the loudspeakers, and the printer.
Simply put, a power supply unit is a hardware device that helps supply power to your electronic system, be it a laptop or desktop. In technical terms, it converts AC to DC to power up your device.
Laptops draw power from smaller PSUs, i.e., anywhere between 30 to 90 watts. That sheds light on the fact that their maximum power consumption is bound to this limit and hence, has lower potential. Not just that, they generally also include substantially slower-performing CPUs and components
In contrast to Laptops, Desktops draw power from larger supply units, i.e., about 300 watts or even more, hence going far beyond their system requirements. Common desktops only require an energy draw of around 170 watts to peak. However, performance desktops may surprise you with their whopping draw of 400 Wh at full load.
When not plugged into an electric socket, your electronic appliance may run on energy stored in the battery. Here is how it differs in Laptops and Desktops:
Laptops are designed in such a way that they can operate solely on battery backup for hours even when not connected to a power outlet. What’s more, they also impress with an extended battery life. The secret behind that is simple: either it already comes with an in-built battery that is larger and more capable or the laptop’s hardware is designed to be more energy efficient or eat up less energy. Any which way, your laptop power usage tends to be relatively less thanks to this.
Desktops usually require a permanent power supply which implies that PC electricity usage is constant, regardless of whether it is in sleep or standby mode. It is often recommended to install a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) to help prevent system crashes during sudden power cuts. It also offers the benefit of power backup to desktop but it is often very limited. However, be prepared to witness higher electricity bills since that also means that you require more power to charge and maintain the UPS’ battery.
The CPUs and other components consume a lot of energy and put out a lot of heat in return. Here is how the energy consumption of laptop vs desktop differs as a result:
The CPUs in Laptops are designed to be substantially slower. Moreover, they also have in-built graphics processing unit that is meant to be more energy-efficient, thus further reducing laptops’ power usage.
The processing units in Desktops, on the other hand, are infamous for consuming relatively more energy.
When an electronic device is plugged in but not actively in use, the energy that it still consumes is known as standby or vampire power. It makes a bigger difference than you may think:
The advantage of operating laptops is that they are designed with power-saving features that allow them to enter low-power states more efficiently than desktop computers. In turn, the laptop energy consumption tends to be less when it is in sleep mode or hibernation.
The advantage in Laptops is the disadvantage in Desktops. They are typically plugged into a power source and not optimized for low-power states. Hence, they may consume more power on stand-by mode.
To keep the long story short, in the battle of the more energy-efficient appliance between laptop and desktop, the former is the clear winner. PCs may come with their fair share of benefits but being energy-efficient isn’t one of them. So, now when you’re looking to cut down on your power bills, turning to laptops should be a no-brainer.
Moreover, Econnex is right by your side to help you compare your electricity and gas rates so you can worry less about your Desktop or Laptop aggravating your power bills! Visit our site for the list of the best energy plans in your area and make the smart switch in a matter of minutes.



